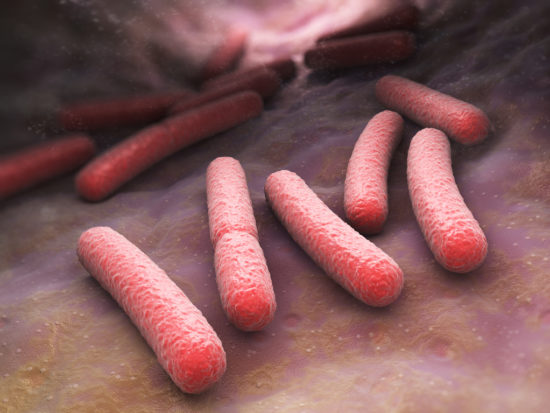
Specialist Enzymes Make E. coli Antibiotic Resistant at Low pH
New research from Washington University in St. Louis suggests that many so-called redundant enzymes are actually specialists that ensure maximal growth across different environments.
Further, these specialist enzymes were found to increase E. coli’s resistance to antibiotics at low pH conditions, such as those found in the GI tract or urinary tract — raising concerns that current antibiotic susceptibility tests are inadequate.
AMR NEWS
Your Biweekly Source for Global AMR Insights!
Stay informed with the essential newsletter that brings together all the latest One Health news on antimicrobial resistance. Delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks, AMR NEWS provides a curated selection of international insights, key publications, and the latest updates in the fight against AMR.
Don’t miss out on staying ahead in the global AMR movement—subscribe now!