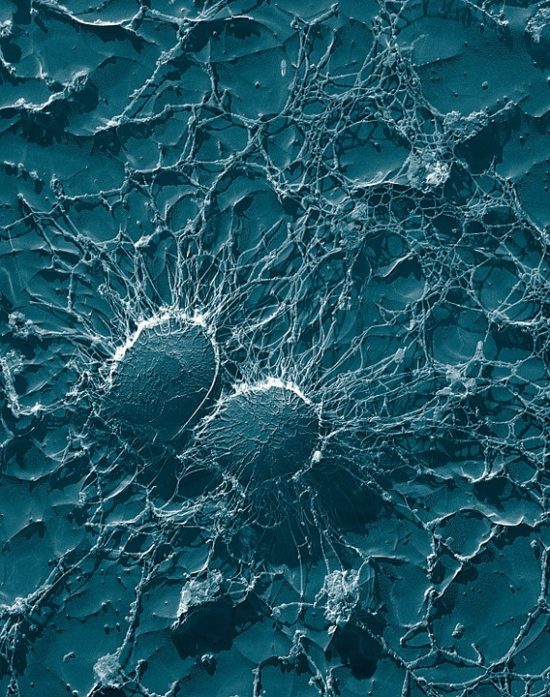
One quarter of bacterial pathogens can spread antibiotic resistance directly to peers
Biomedical engineers at Duke University have demonstrated that at least 25 percent of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria found in clinical settings are capable of spreading their resistance directly to other bacteria. At the same time, the study shows that, despite common beliefs, the use of antibiotics does not significantly affect the rate at which the genes responsible for resistance are swapped between bacteria.
Researchers used a new high-throughput method of measuring the rate at which bacteria exchange the packages of DNA that bestow resistance. The speed and ability to automate much of the process could allow new insights into what variables affect transfer rates. Such efforts could help doctors slow—or even reverse—the spread of resistance in certain human pathogens.
AMR NEWS
Your Biweekly Source for Global AMR Insights!
Stay informed with the essential newsletter that brings together all the latest One Health news on antimicrobial resistance. Delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks, AMR NEWS provides a curated selection of international insights, key publications, and the latest updates in the fight against AMR.
Don’t miss out on staying ahead in the global AMR movement—subscribe now!