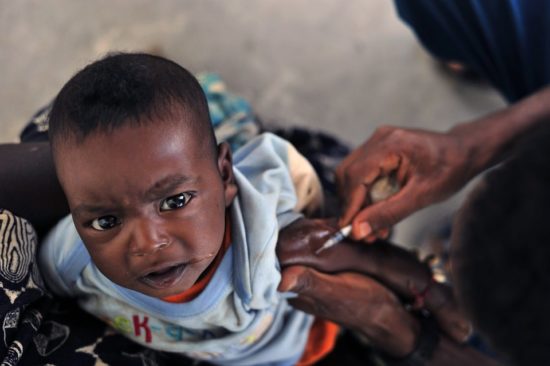
Multidrug-resistant iNTS: A growing threat in Kenya
Drug resistance is a significant and growing problem across the world for many bacterial infections, from tuberculosis to bacterial pneumonia, typhoid, invasive nontyphoidal Salmonella (iNTS) disease, and more. Antibiotics, medicines used to treat bacterial infections, have been a cornerstone of modern medicine since they were discovered. Unfortunately, due to overuse and misuse, as well as the natural evolution of bacteria, many of the antibiotics available to treat these diseases are becoming ineffective.
This problem is particularly concerning for iNTS, which has no vaccine available to prevent it. iNTS is a major public health challenge that impacts communities in sub-Saharan Africa the hardest. It can be caused by many different nontyphoidal Salmonella strains, with Salmonella Typhimurium and Salmonella Enteritidis being the most common. Young infants and children younger than 5 years of age often bear the brunt of the burden, accounting for 65 percent of cases in the region. When left untreated, iNTS can be fatal 20 to 25 percent of the time, underscoring the importance of prompt, appropriate, and effective antibiotic treatment.
AMR NEWS
Your Biweekly Source for Global AMR Insights!
Stay informed with the essential newsletter that brings together all the latest One Health news on antimicrobial resistance. Delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks, AMR NEWS provides a curated selection of international insights, key publications, and the latest updates in the fight against AMR.
Don’t miss out on staying ahead in the global AMR movement—subscribe now!