Isolation and characterization of lytic bacteriophages from various sources in Addis Ababa against antimicrobial-resistant diarrheagenic Escherichia coli strains and evaluation of their therapeutic potential
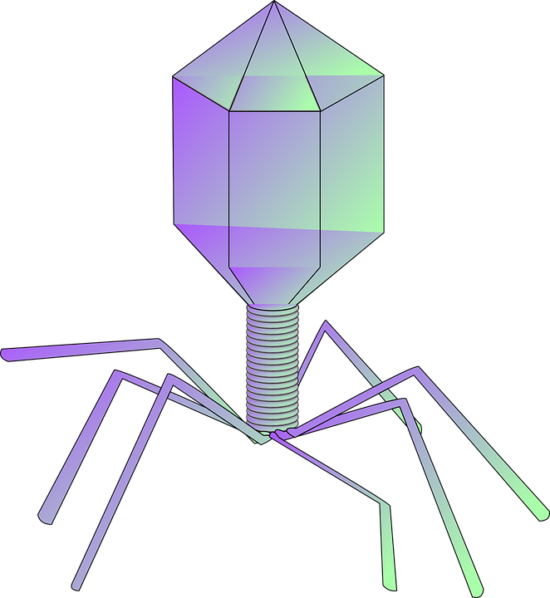
This study aimed to isolate and characterize lytic bacteriophages from various sources in Addis Ababa, test them against antimicrobial-resistant diarrheagenic E. coli strains, and evaluate their therapeutic potential under in vitro conditions. A total of 17 phages were recovered from 84 tested plates, with 7 potent phages selected based on host range test, growth characteristics, and stability tests. These phages demonstrated better growth characteristics, short latent periods, highest burst sizes, wider host ranges, thermal stability, and ability to survive in various pH levels. The promising effect of these phages against AMR pathogenic E. coli has raised the possibility of their use in future E. coli infections.
AMR NEWS
Your Biweekly Source for Global AMR Insights!
Stay informed with the essential newsletter that brings together all the latest One Health news on antimicrobial resistance. Delivered straight to your inbox every two weeks, AMR NEWS provides a curated selection of international insights, key publications, and the latest updates in the fight against AMR.
Don’t miss out on staying ahead in the global AMR movement—subscribe now!